To achieve reliable visual testing, it’s crucial to prevent unreliable tests by effectively hiding dynamic parts of your application.
When dealing with elements prone to change, like ad banners, moving text inputs, GIFs, and user cursors, it’s essential to use dynamic element masking. This means hiding these elements before taking screenshots during testing to avoid false results due to dynamic content.
Let’s use an example and imagine we want to assess the layout of the Facebook Stories section through visual testing.

The challenge here is that the images and titles in the stories tray element will differ whenever you reload the page. This isn’t ideal for visual testing.

Modern testing frameworks provide methods for this. For instance, Playwright lets you hide specific page elements when taking screenshots by completely covering its bounding box with a #FF00FF color.
Let’s try to hide all <img> elements before making a screenshot.
let mask_locator = page.locator("//img")
await page.screenshot({path: 'masked.png', mask: [mask_locator]})The problem with such an approach is that it completely covers your element bounding box, so since every HTML element is a rectangle, you will see something like that.

Default Playwright masking is excellent for simple rectangle ad banners and buttons, but you want something better and more accurate for complex layouts.
For instance, you can toggle the visibility of images in this section because they aren’t necessary for layout testing. To implement this, please review the script provided below.
// Get all img elements on the page
var imgElements = document.getElementsByTagName('img');
// Loop through each img element and hide it
for (var i = 0; i < imgElements.length; i++) {
imgElements[i].style.display = 'none';
}
// Get the element with aria-label="stories tray"
var storiesTray = document.querySelector('[aria-label="stories tray"]');
// Check if the stories tray element exists
if (storiesTray) {
// Get all span elements inside the stories tray
var spanElements = storiesTray.querySelectorAll('span');
// Loop through each span element inside the stories tray and replace its text content with "test."
spanElements.forEach(function(span) {
span.textContent = 'test';
});
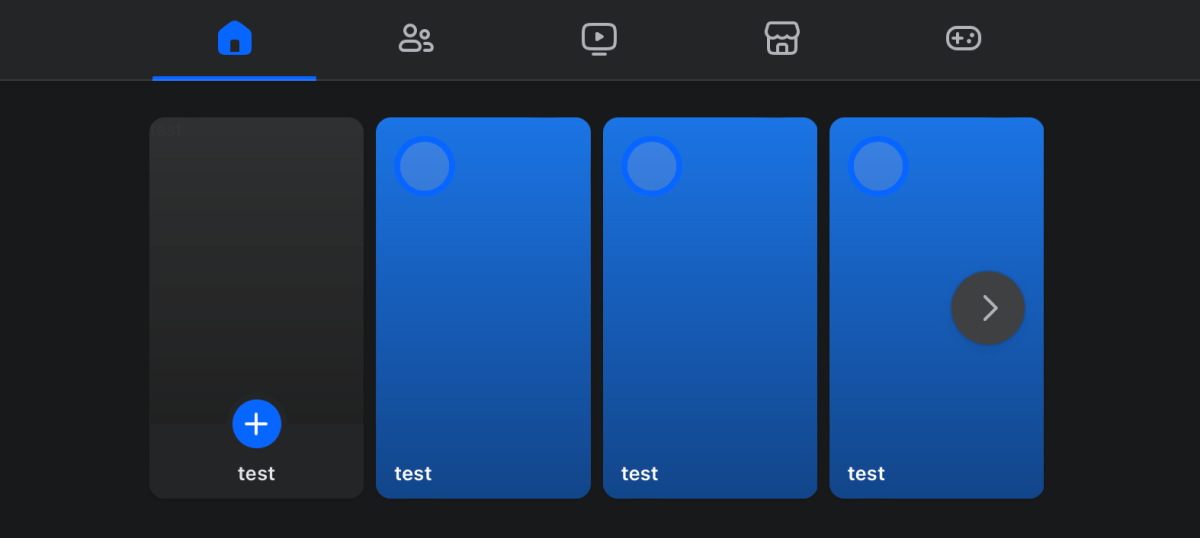
}This script hides all <img> elements and changes the story titles into “test” because we don’t need to check the text value, just a layout.
After executing such a script, the section will resemble a clean layout that you can capture in a screenshot and use for comparison in your visual tests.

If you don’t want to hide such elements or want to highlight hidden areas, you can fill it with any color, i.e., #FF00FF, using the next script:
// Get all img elements on the page
const imgElements = document.querySelectorAll('img');
// Loop through each img element and set its background color to red
imgElements.forEach((img) => {
img.style.backgroundColor = '#FF00FF';
img.src = ''; // Optional: Remove the image source to hide the original image
});
// Get the element with aria-label="stories tray"
var storiesTray = document.querySelector('[aria-label="stories tray"]');
// Check if the stories tray element exists
if (storiesTray) {
// Get all span elements inside the stories tray
var spanElements = storiesTray.querySelectorAll('span');
// Loop through each span element inside the stories tray and replace its text content with "test"
spanElements.forEach(function(span) {
span.textContent = 'test';
});
}
Embracing this technique ensures stable and trustworthy visual tests, allowing you to detect real issues without distractions from transient visual elements.

